Development in health and social care is all about improving the quality of care that individuals receive. Whether it’s through the introduction of new technologies, better training for staff, or improved policies, development in this sector ensures that patients get the best possible treatment. The healthcare landscape is constantly changing, and so must the services that support people’s health and well-being.
At its core, development in health and social care is about making care more patient-centred, accessible, and effective. It means finding new ways to meet the needs of individuals and communities, especially as those needs evolve over time. By focusing on continual improvement, the goal is to create a system that delivers better outcomes for everyone, no matter their circumstances.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of development in health and social care and why it’s essential for building a system that works for everyone, now and in the future.
1. What Is Development In Health And Social Care?
Development in health and social care refers to the continuous process of improving services, practices, and outcomes within the healthcare and social care sectors. It encompasses a range of activities aimed at enhancing the quality of care provided to individuals, the professional growth of healthcare workers, and the efficiency of healthcare systems. Development can take many forms, such as training and upskilling professionals, introducing new technologies, expanding healthcare services, and improving organisational structures and policies.
The goal of development in health and social care is to ensure that care is responsive to the changing needs of populations, advances in medical knowledge, and emerging health challenges. It focuses on improving patient outcomes, enhancing the overall experience of care, and adapting systems to be more efficient, inclusive, and sustainable.
2. What is Continuing Professional Development in Health and Social Care?
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) in health and social care refers to the ongoing process by which healthcare and social care professionals enhance their knowledge, skills, and competencies throughout their careers. CPD ensures that individuals stay up-to-date with the latest developments, practices, and technologies in their field, enabling them to deliver high-quality, effective care.
CPD can take many forms, including attending workshops, participating in training sessions, enrolling in online courses, and even self-directed learning. For healthcare professionals such as nurses, doctors, care workers, and social workers, CPD is often a mandatory requirement to maintain their professional registration and ensure their practices align with current healthcare standards.
The purpose of CPD in health and social care is to promote a culture of lifelong learning and improvement, allowing professionals to adapt to new treatments, technologies, and approaches to patient care. It helps improve patient outcomes, ensures safe and effective care, and supports career progression by opening up opportunities for specialisation and leadership roles. Ultimately, CPD plays a crucial role in ensuring that the health and social care workforce remains competent, knowledgeable, and able to meet the evolving needs of patients and clients.
3. Personal Development in Care Settings

Personal development in care refers to the process of individuals working in health and social care services. Developing skills, knowledge and self-awareness To increase our ability to provide compassionate and effective care. It is an important part of professional growth. It focuses on the professional and personal aspects that contribute to providing high quality care
Personal development in clinical settings includes activities such as coaching, reflection, and self-assessment. This helps care staff understand their strengths and areas for improvement. Builds interpersonal skills such as empathy, communication, and teamwork. This is essential to developing trusting relationships with patients, customers, and co-workers.
Personal development also supports care professionals in managing the emotional and physical demands of work. By promoting self-awareness time management and stress management skills Care workers can simultaneously maintain their own well-being. and improve the care provided to others. In addition, personal development creates opportunities for career advancement. Because each person has more responsibility. and carry out the leadership role or specialise in care Increase confidence and ability.
4. Leadership Development in Healthcare
Leadership development in healthcare refers to the process of enhancing the skills, knowledge, and abilities of individuals to effectively lead teams, drive innovation, and improve patient care within healthcare organisations. Strong leadership is essential in healthcare because it helps to manage complex systems, guide multidisciplinary teams, and ensure high-quality, safe care for patients.
Leadership development programs in healthcare focus on building competencies in areas such as communication, decision-making, conflict resolution, and strategic planning. These programs often involve mentorship, training courses, workshops, and experiential learning opportunities to equip healthcare professionals with the tools needed to inspire and manage teams, make informed decisions, and adapt to the rapidly changing healthcare environment.
In healthcare settings, leadership is not limited to those in senior management positions; it includes frontline healthcare workers such as doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals who take on leadership roles within their teams or departments. Leadership development helps these individuals cultivate skills in managing patient care, leading quality improvement initiatives, and advocating for patient safety and well-being.
Effective leadership is crucial in healthcare as it ensures that healthcare services are delivered efficiently, staff are well-supported, and the organisation can respond effectively to challenges such as resource constraints, policy changes, or public health crises. By investing in leadership development, healthcare organisations promote a culture of continuous improvement, collaboration, and accountability, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a more resilient healthcare system.
5. What Are The 4 Areas of Development in Health and Social Care?
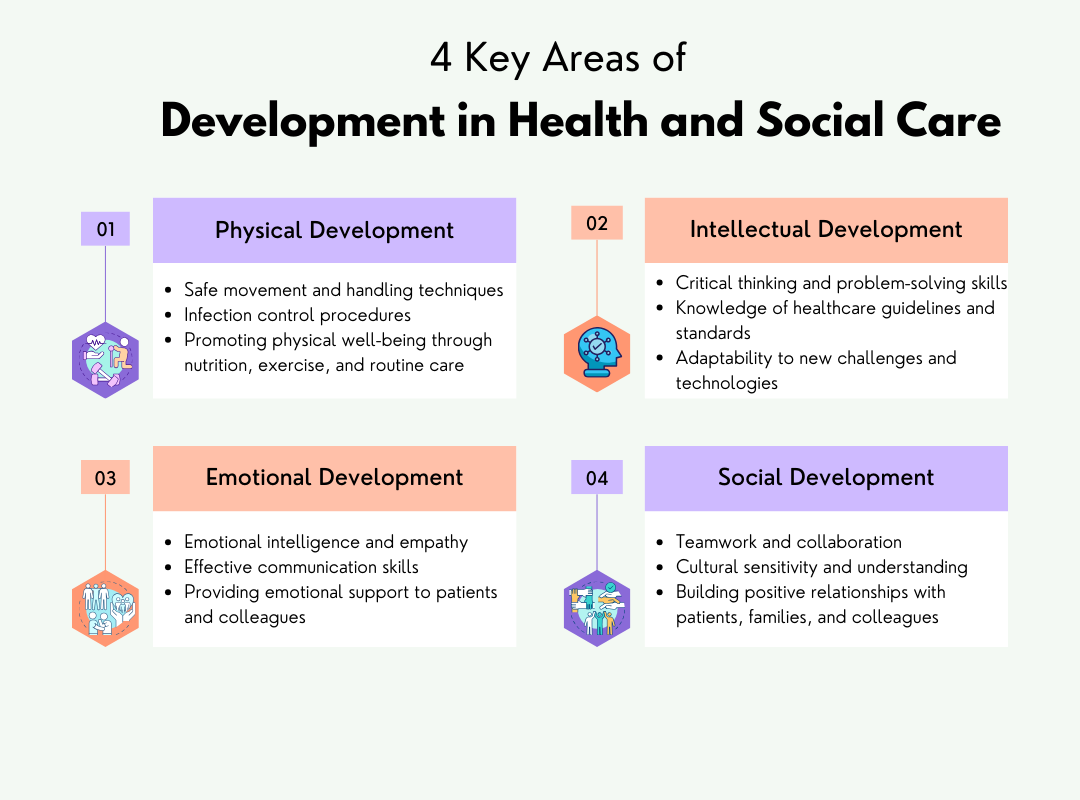
The 4 key areas of development in health and social care are:
Physical Development
Physical development in health and social care entails developing practical skills to improve the physical well-being of patients and workers. This involves learning safe movement and handling skills to avoid harm when supporting people with mobility, as well as infection control procedures to preserve cleanliness and prevent the transmission of sickness. It also entails learning how to enhance physical health via adequate nutrition, exercise, and routine care so that individuals may preserve their physical health and freedom.
Intellectual Development
Intellectual development focuses on sharpening your critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, which are essential for making informed decisions in complex healthcare situations. It also involves keeping up with relevant healthcare guidelines and standards to ensure safe and effective care. Expanding your knowledge of policies, procedures, and best practices is crucial for adapting to new challenges, treatments, and technologies in the healthcare environment.
Emotional Development
Emotional development is about building emotional intelligence, which allows healthcare professionals to understand and manage their own emotions while being empathetic toward others. It also involves improving communication skills to ensure clear, compassionate interactions with patients, families, and colleagues. Being emotionally aware helps healthcare professionals provide emotional support, especially when dealing with sensitive situations or individuals going through stressful or difficult times.
Social Development
Social development improves your capacity to collaborate by encouraging collaboration and conflict resolution abilities. In health and social care settings, good teamwork is critical for providing complete care. Cultural sensitivity is another aspect of social development that allows professionals to comprehend and appreciate the varied backgrounds of their patients and colleagues. These abilities assist in developing strong, productive connections, encouraging inclusion, and providing person-centred care.
6. How is Development Measured in Health and Social Care?

Development in health and social care is measured using a variety of approaches that examine individual growth, efficacy, and quality of treatment. These metrics guarantee that both healthcare professionals and companies are always striving to satisfy the demands of patients and customers. The following are the primary methods in which development is measured in health and social care:
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction
Health Outcomes: The success of treatment and interventions is often measured by tracking patient outcomes. This includes improvements in health conditions, recovery rates, reductions in hospital readmissions, and the management of chronic diseases.
Patient Satisfaction: Surveys and feedback from patients help measure their experiences with healthcare services. Positive patient satisfaction scores indicate that development efforts are meeting the needs of the individuals receiving care.
Professional Competence and Training
Continuing Professional Development (CPD): Healthcare professionals are required to engage in ongoing education and training. CPD logs and certifications track their development, ensuring they are up-to-date with the latest practices, guidelines, and technologies.
Skill Assessments and Performance Reviews: Regular assessments and appraisals evaluate the skills and competencies of healthcare professionals, ensuring that they are providing quality care and are continually improving in their roles.
Clinical Audits and Benchmarking
Clinical Audits: Audits are conducted to assess whether care meets established standards and protocols. By reviewing patient records, procedures, and outcomes, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement and measure progress over time.
Benchmarking: Comparing performance metrics with national or industry standards helps measure how well a healthcare organisation or service is performing relative to others. Benchmarking can highlight gaps in care and areas where further development is needed.
Quality of Care Indicators
Safety and Compliance Metrics: The frequency of safety incidents, such as medication errors or hospital-acquired infections, are key indicators of the quality of care. Lower rates of such incidents indicate positive development in safety practices.
Regulatory Compliance: Regular inspections by regulatory bodies, such as the Care Quality Commission (CQC) in the UK, assess whether healthcare providers meet required standards. Achieving high ratings in areas like safety, effectiveness, and responsiveness is a measure of ongoing development.
Team Performance and Collaboration
Teamwork and Collaboration: The effectiveness of teamwork is measured through outcomes related to multidisciplinary collaboration. How well healthcare teams communicate and work together is crucial for delivering coordinated care and improving patient outcomes.
Staff Engagement and Retention: Measuring employee satisfaction and retention rates can indicate how well staff development initiatives, such as training, career progression, and leadership development, are working.
Service Delivery and Accessibility
Service Efficiency: Metrics like wait times, the availability of services, and patient throughput are used to measure how effectively healthcare services are delivered. Improvements in these areas indicate positive development in service delivery.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Ensuring that healthcare services are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities or from underserved communities, is a key measure of development. Expansion of services to reach more people, such as through telehealth or mobile clinics, reflects progress.
7. Factors Affecting Development
Development in health and social care is influenced by a variety of factors that can either facilitate or hinder progress in delivering quality care. Here are some of the key factors affecting development in health and social care:
Funding and Resources
Adequate funding is crucial for investing in technology, staff training, and infrastructure. Limited resources can slow progress in delivering quality care, especially in underserved areas.
Workforce Development
Continuous professional development and sufficient staffing levels ensure that healthcare workers are skilled and able to adopt new practices, improving patient care.
Technological Advancements
Access to and adoption of innovations like telehealth, electronic records, and modern equipment drive improvements in care delivery and efficiency.
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks
Government policies and regulations shape the healthcare environment. Supportive policies foster development, while restrictive ones can hinder progress.
Patient Demographics and Needs
Changing population needs, such as aging or chronic illness trends, require healthcare services to adapt, driving development in care practices.
Leadership and organisational Culture
Strong leadership and a culture that embraces innovation and collaboration encourage continuous improvement and development.
Public Perception and Patient Engagement
Patient expectations for better service and involvement in care push healthcare providers to innovate and improve services.
Social and Economic Inequalities:
Health disparities and geographical barriers affect access to care, slowing development. Targeted solutions like telemedicine help bridge these gaps.
8. Promoting Development in Health and Social Care

Promoting development in health and social care is essential for improving services, enhancing patient outcomes, and adapting to evolving needs. Here are key strategies to foster development:
Invest in Training and Professional Development
Ongoing training and upskilling ensure that healthcare professionals are equipped with the latest knowledge, techniques, and best practices. Encouraging Continuing Professional Development (CPD) helps build a skilled workforce that can deliver high-quality care.
Adopt New Technologies
Embracing innovations like telehealth, electronic health records (EHRs), and AI-driven diagnostics enhances efficiency and patient care. Investing in modern technology allows healthcare providers to stay competitive and meet evolving patient needs.
Foster Strong Leadership
Effective leadership drives growth and innovation. By developing leadership skills at all levels, healthcare organisations can create a culture of continuous improvement, collaboration, and responsiveness to change.
Encourage Collaboration and Teamwork
Multidisciplinary teams are key to delivering comprehensive care. Promoting collaboration between doctors, nurses, social workers, and support staff helps improve patient care and fosters innovation in care practices.
Focus on Patient-centred Care
Engaging patients in their care decisions and focusing on patient-centred services encourages better outcomes and satisfaction. Involving patients in feedback and service design can lead to more effective and personalised care.
Improve Infrastructure and Resources
Investing in healthcare infrastructure, such as upgrading facilities and ensuring access to necessary equipment, supports better service delivery. Adequate resources help maintain high standards of care.
Advocate for Policy Support
Government policies play a significant role in shaping healthcare development. Advocacy for policies that support increased funding, innovation, and access to healthcare services ensures long-term growth and improvement.
Address Social and Economic Inequalities
Implementing initiatives to reduce health disparities, such as improving access to care in rural or underserved areas, helps promote equity in healthcare services. Tailored approaches to marginalised populations can drive development by ensuring everyone benefits from advancements in care.
9. FAQ
1. What does development in health and social care involve?
Development in health and social care focuses on improving the quality of care, enhancing professional skills, integrating new technologies, and adapting services to meet changing patient needs. It aims to ensure efficient, inclusive, and sustainable healthcare.
2. Why is ongoing professional development essential for healthcare workers?
Ongoing professional development ensures that healthcare workers stay current with advancements in care, techniques, and regulations. It helps improve patient outcomes, maintain professional standards, and create opportunities for career progression.
3. What are the key areas of development in health and social care?
The main areas of development are:
- Physical: Improving practical care skills and patient well-being.
- Intellectual: Enhancing problem-solving and decision-making abilities.
- Emotional: Developing empathy, emotional intelligence, and communication.
- Social: Fostering teamwork, collaboration, and cultural understanding.
4. How can we measure progress in health and social care development?
Progress is measured through patient outcomes, feedback, staff training, clinical audits, and regulatory compliance. These indicators help assess the quality of care, effectiveness of services, and areas where improvement is needed.
5. What are effective ways to promote development in healthcare services?
Effective ways to promote development include continuous staff training, adopting new technologies, fostering leadership, improving infrastructure, promoting patient-centred care, and addressing inequalities in healthcare access.
10. Conclusion
Development in health and social care is critical for improving patient outcomes, honing professional abilities, and adjusting to societal demands. We can develop a more effective and fair healthcare system by emphasising continuous learning, embracing technology, and tackling critical obstacles such as funding and disparities.
Finally, fostering development ensures that healthcare services adapt to suit the needs of all people, regardless of their situation. It is up to healthcare professionals, legislators, and communities to accelerate development and create a future in which high-quality care is available to all.



















