Imagine walking into a care setting where every resident’s needs are met with precision, respect, and care. That’s the power of a well-executed care plan. According to Skills for Care, 70% of carers in the UK report that care plans directly impact the quality of care they provide. This makes care planning essential in ensuring residents receive the best support.
Care planning policy outlines guidelines for creating personalised care plans, ensuring that each individual receives tailored support based on their needs, preferences, and goals. It guides professionals in providing consistent, high-quality care while respecting individual choices and promoting wellbeing.
With that in mind, by reading this blog, let’s look at what we will explore further:
- What care planning policy is
- The key components of care planning
- The role of social care professionals in the care planning process
- Practical insights into how to apply care planning policies effectively in your work.
What is Care Planning Policy?
Care planning policy is a set of guidelines used to create structured, personalised care plans for individuals in health and social care. It ensures that care providers meet the specific needs, preferences, and goals of each person. By outlining clear steps, the policy helps professionals deliver care that is consistent, high-quality, and respectful of individual choices.
This policy makes sure that care is provided in a way that meets both physical and emotional needs, ensuring each person’s dignity and autonomy are respected. It is essential for making sure that all care plans are properly documented and that everyone involved in the care process is on the same page.
The Role of Care Planning Policy in Ensuring Quality Care
Care planning policy is fundamental to delivering high-quality care that meets individual needs. It serves as a framework for care providers, making sure they follow standardised procedures when creating care plans. The policy helps care teams focus on the person receiving care, ensuring that their needs are addressed consistently and comprehensively.
- Personalisation: Care planning policy ensures that each individual’s plan is specific to their needs and preferences, rather than a generic approach.
- Clear communication: The policy encourages clear documentation of care plans, so all team members understand their responsibilities.
- Safety: It prevents mistakes by providing a step-by-step approach to care, helping carers make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
By adhering to care planning policy, care providers can deliver more effective, tailored care that promotes better health outcomes and a greater sense of well-being for those receiving care.
Health and Social Care Level 3 Diploma
How Care Planning Policy Supports Person-Centred Care
Person-centred care focuses on respecting and empowering individuals to take an active role in decisions about their care. Care planning policy plays a key role in promoting this approach by ensuring that care plans are centred around the individual’s preferences, goals, and values.
- Respect for choice: The policy empowers individuals to make decisions about their own care, ensuring that their choices are respected and incorporated into their care plans.
- Better health outcomes: When care is personalised and responsive to individual needs, it leads to more positive physical, mental, and emotional outcomes.
- Engagement: Person-centred care promotes stronger relationships between care providers and recipients, fostering trust and improving the overall care experience.
By following care planning policy, professionals create a supportive environment where people receiving care feel heard, valued, and involved in their own care journey. This approach not only enhances their quality of life but also ensures that they receive care that is truly meaningful and effective.
The Importance of Person-Centred Care in Care Planning
What is Person-Centred Care?
Person-centred care is an approach that places the individual at the heart of their care. It focuses on treating each person as a unique individual, respecting their preferences, values, and needs. This approach ensures that care plans are developed with the active involvement of the person receiving care, allowing them to make informed decisions about their own care. Rather than just focusing on medical conditions, person-centred care acknowledges the physical, emotional, and social aspects of a person’s well-being.
How Person-Centred Care Fits into Care Planning
Person-centred care is a core principle in care planning because it ensures that each individual receives care that is tailored to their specific needs and preferences. It goes beyond just meeting basic health requirements, aiming to enhance the person’s overall quality of life by addressing emotional and psychological well-being as well. This approach is fundamental in care settings because it ensures the dignity and autonomy of the person receiving care, making them an active participant in their care journey.
- Empowering individuals: Person-centred care promotes choice and control, allowing individuals to have a say in decisions regarding their care and daily routines.
- Improved care outcomes: By focusing on the individual, person-centred care helps achieve better health outcomes, higher satisfaction, and a more positive experience for both care recipients and providers.
- Enhanced relationships: The approach fosters trust and better communication between caregivers and residents, helping build stronger, more supportive relationships.
Steps in in the Care Planning Process
The care planning process involves several stages that ensure individuals receive the most appropriate and personalised care. Here’s a simple breakdown of each step:
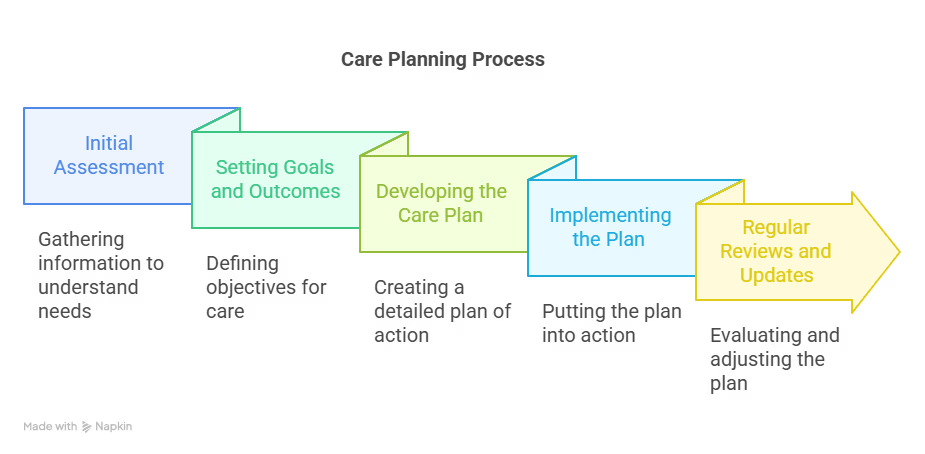
Initial Assessment
The first stage involves gathering information about the individual’s health, needs, preferences, and lifestyle. This includes both physical and mental health conditions, as well as any social needs. The assessment helps to identify the level of care required and forms the basis for creating a tailored care plan.
Setting Goals and Outcomes
Once the assessment is completed, the next step is to define clear, achievable goals. These goals should focus on improving the person’s quality of life and addressing their specific health conditions. This could include goals related to physical health, emotional wellbeing, or independence.
Developing the Care Plan
Based on the assessment and goals, a detailed care plan is created. The plan outlines the services and support needed, such as medical care, daily assistance, or therapeutic activities. It ensures that every aspect of the person’s wellbeing is considered, including their preferences, cultural background, and any ongoing treatments or therapies.
Implementing the Plan
This stage involves putting the care plan into action. Caregivers and healthcare professionals deliver the planned services, regularly checking in with the individual to ensure their needs are being met. This is where collaboration between different care providers is essential for seamless care.
Regular Reviews and Updates
Care plans should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain relevant and effective. As health conditions change or new needs arise, the plan must be adjusted to reflect these changes. Regular updates are crucial for addressing long-term care needs and ensuring that care is always in line with the person’s evolving requirements.
Importance of Regular Updates
Continuous monitoring and review are vital for long-term care. As conditions like dementia, chronic illnesses, or physical disabilities progress, care plans must be adapted. Regular updates ensure that health conditions are consistently addressed, reducing the risks of health complications and improving overall care outcomes. By keeping the care plan flexible and dynamic, care providers can offer more responsive, high-quality care.
Ultimately, the care planning process helps create a comprehensive, person-centred approach, where individuals are actively involved in decisions regarding their care.
Creating Personalised Care Plans
Personalised care plans are at the heart of providing effective care. Social care professionals play a crucial role in creating these plans by tailoring them to meet the individual needs, preferences, and goals of each resident or service user. These plans aren’t just about addressing medical conditions but about understanding the person as a whole – considering their physical, emotional, and social needs.
Role of Social Care Professionals
Social care professionals, such as care managers and care assistants, are responsible for assessing the needs of the individual and then designing a care plan that suits them. This process involves working closely with the person receiving care, their family, and any other professionals involved, ensuring that all aspects of their wellbeing are taken into account. Social care professionals must listen carefully to their clients, respecting their views and preferences to create a care plan that is meaningful and relevant to them.
Significance of Personalised Goals and Preferences
The heart of a personalised care plan lies in setting goals that are tailored to the individual. Personalised goals are not just about health outcomes—they also reflect what’s most important to the person. For example, a person may want to maintain their independence for as long as possible, while another may prioritise social interaction or participation in specific activities.
Including personal preferences in care planning ensures that the person is not just receiving generic care, but care that aligns with their values, routines, and interests. By incorporating these goals, caregivers can help individuals maintain a sense of dignity and control over their lives. Moreover, this personalised approach helps to enhance emotional wellbeing, encourages active participation, and improves overall satisfaction with the care provided.
In short, when care plans are tailored to the person, they are more likely to lead to positive outcomes, making the person feel respected, valued, and empowered.
The Role of Health and Social Care Professionals in Care Planning

Social care professionals play a vital role in the development and implementation of care planning policies. Their expertise helps ensure that care plans are tailored to meet the specific needs of individuals. By understanding the person’s background, preferences, and health conditions, they can create plans that promote the best possible outcomes. Social care professionals use a person-centred approach to ensure that care is not just about managing medical conditions but also about enhancing the individual’s quality of life and maintaining their dignity.
Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals
Collaboration is key in care planning. Health and social care professionals—such as doctors, nurses, care assistants, and social workers—must work together to create a comprehensive care plan that addresses all aspects of an individual’s health and wellbeing.
By sharing knowledge and expertise, these professionals can ensure that care plans are holistic and coordinated. For example, a nurse may provide insights into the medical needs of a resident, while a social worker can consider emotional and social factors.
This collaboration ensures that no aspect of the individual’s care is overlooked, and that every professional involved is aligned with the overall care strategy. It’s crucial that these professionals communicate effectively and update each other regularly to adapt to any changes in the individual’s needs or circumstances. Working as a team not only improves the quality of care but also ensures a more streamlined and efficient process, leading to better outcomes for residents.
How Care Planning Aligns with Health Conditions and Long-Term Care
Care planning is key in managing long-term health conditions. It ensures that care is tailored to the individual’s needs, which is crucial for conditions like diabetes, dementia, or heart disease. A care plan helps track symptoms, treatments, and progress, while also addressing emotional and social wellbeing. This comprehensive approach helps prevent complications and ensures that the person receives the right support at every stage of their health journey.
The Importance of Flexibility in Care Plans
As health conditions can change, having a flexible care plan is important. A care plan should be able to adapt as the person’s needs evolve. This could mean adjusting treatments, medications, or care routines. Regular reviews make sure that the plan stays up to date and continues to provide the most relevant care. A flexible approach helps ensure that the person’s needs are always met, making long-term care more effective and supportive.
FAQs
What are the 5 stages of care planning?
The five stages of care planning include assessment, where a person’s needs are understood; care planning, where goals are set; implementation, where the plan is put into action; review, to ensure the plan is working; and evaluation, to make necessary adjustments.
What are the 5 main components of a care plan?
The five main components of a care plan are personal information, to know the individual’s background; health conditions, to address specific needs; goals and outcomes, to measure success; care interventions, to define the actions to be taken; and monitoring and reviews, to ensure progress.
What are the 4 types of care plans?
The four types of care plans are individual care plans, focusing on the personal needs of one person; family care plans, involving families in the care process; medical care plans, centred on medical needs; and holistic care plans, addressing all aspects of the person’s well-being.
What are the 4 key steps to care planning?
The four key steps to care planning involve assessing needs, setting clear care goals, creating a plan of action, and regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan to ensure it meets the individual’s needs.
Final Words
Care planning ensures that individuals receive personalised, high-quality care tailored to their needs and preferences. By following structured stages—from assessment to regular reviews—care plans help address both immediate and long-term health conditions effectively.
For new professionals, engaging in continuous learning and applying care planning policies will enhance your ability to provide compassionate, effective care. Stay informed and adaptable to meet the evolving needs of those you support.